 Server - a computer separated from the group of personal computers (or workstations) to perform any service task without the direct participation of a person. Servers and workstations can have the same configuration because they differ from each other only in their work with the human console.
Server - a computer separated from the group of personal computers (or workstations) to perform any service task without the direct participation of a person. Servers and workstations can have the same configuration because they differ from each other only in their work with the human console.
The server device is often designed to provide continuous (24/7) service operation, so it is often staffed with duplicate elements.
Server memory provides high resistance to fraud.
Enhanced server reliability is achieved through backups, including "hot connection" and replacement of critical components (Hot-swap):
- Duplicate processors if necessary;
- Power blocks;
- Hard disks within the RAID array and the disk controllers themselves;
- Groups of fans that provide cooling to the server components.
The hardware monitoring functions include additional channels to control a large number of server settings: the temperature transmitter controls the temperature mode of all processors, memory modules, the temperature in the areas where the hard drives are installed; Electronic pulse meters, which are built into the fans, perform the functions of tachometers and allow, depending on the temperature, to regulate their rotational speed; Constant control of the supply voltage of the server components enables the alarm on the efficiency of the operation of the power units; The watch timer allows the system to be "hung" unnoticed and automatically restarts the server internally.
Exterior performance measures and other details.
Servers (and other devices that need to be installed on a standard chassis (for example, in 19-inch stands and cabinets) require standard dimensions and the necessary support elements.
Constructed hardware servers can be implemented as desktop, floor or stand options. The latter option provides the maximum density of computing power per unit area, as well as maximum scaling. Since the late 1990s, high-reliability and scaling systems have become increasingly popular. Blade servers (English blade - sharp person). These are compact modular devices that can reduce the cost of electricity, cooling, service and related costs.
Data storage system (DSS)
 Data storage system (DSS) - is a complex software-hardware solution for organizing reliable storage of information resources and giving them guaranteed access.
Data storage system (DSS) - is a complex software-hardware solution for organizing reliable storage of information resources and giving them guaranteed access.
Among the production systems, we must first distinguish the storage hardware systems: hard disk arrays, their so-called RAID controllers, storage tape systems for long-term storage of data. In addition, a separate class: controllers for storage systems, for data backup management, for creating "snapshots" in the data protection system for their subsequent recovery, data replication and other purposes. Data protection systems also include network devices (HBA, Fiber Channel Switching, FC / SAS cables, and the like) and, finally, developed disaster recovery solutions for data storage, archiving, data recovery, and disasters.
How do we get the data that needs to be stored? From us, our favorite users, applications, emails as well as various devices - file servers and database servers. In addition, a large amount of data providers are so-called. M2M device (Machine-to-Machine communication) - various types of switches, sensors, cameras and accessories).
Depending on the frequency of use of stored data, data storage systems can be divided into short-term storage systems (online storage), medium-term storage systems (near-line storage) and long-term storage systems. (offline storage).
The first can be attributed to the hard drive of any personal computer. Second and third - External storage systems (DAS) (Direct Attached Storage), which can be an array of external disks (Disk Array) to the computer. They, in turn, can be divided into JBOD (Just a Bunch Of Disks) and iDAS (intelligent disk array storage) arrays with a controller.
There are three types of external storage systems: DAS (Direct Attached Storage), SAN (Storage Area Network) and NAS (Network attached Storage). Unfortunately, even many experienced IT specialists can not explain what the difference is between a SAN and a NAS, and say that once this difference once existed, now it seems as if it no longer exists. In fact, the difference is significant. (See Fig. 1).
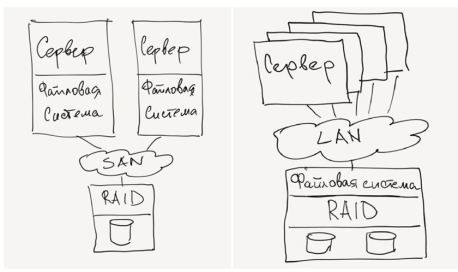
Figure 1. Difference between SAN and NAS.
In a SAN storage system, the data storage network of the SAN is actually connected to the servers themselves. In the case of a NAS, network servers are connected to a LAN system in a RAID file system.